Saul
Mo | Tu | We | Th | Fr | Sa | Su |
Saul - Georg Friedrich Händel
Oratorio in three acts
Libretto by Charles Jennens based on the 1st and 2nd Book of Samuel
Performed in English with German and English supertitles
Premiere: June 1, 2025
Saul and David: when the struggle for power blows a family apart.
Synopsis
The libretto is freely adapted from the First Book of Samuel, Chapters 16–31, with additional material from the epic poem, the Davideis by Abraham Cowley. The printed libretto of Saul from 1738 credits the Davideis as the source of the contemptuous treatment of David by Princess Merab.
Act 1
The Israelites raise their voices in magnificent thanksgiving to God, for the young warrior David has slain the Philistine giant Goliath. At the court of King Saul, once a mighty warrior himself, all the people celebrate the hero David. Saul's son, Jonathan swears eternal devotion to David, but Saul's two daughters experience contrasting emotions – Michal is in love with David, but Merab feels contempt for him as a social inferior, a feeling that only increases when Saul offers her in marriage to David. A group of Israelite young women offer further tributes to David. King Saul is enraged at the way David is praised. Unable to restrain his anger, he orders Jonathan to kill David.
Act 2
The people of Israel reflect on the destructive power of envy. Jonathan pleads David's case to Saul, who appears to relent. Saul asks Jonathan to bring David back to court and promises Michal as David's bride, though Saul anticipates David's death in battle. David and Michal express their mutual love, but David reports that Saul's rage has not diminished and that Saul threw a javelin close past his head in frustration. Saul summons David to court again as both Michal and Merab express their faith that God will protect David. Jonathan tries to explain to Saul why David has not responded to his summons. Saul rages against both David and Jonathan.
Act 3
In despair, and though aware it is unlawful, Saul asks the Witch of Endor to raise the ghost of Samuel the prophet. Asked for advice, the ghost of Samuel reminds Saul that he had once predicted his downfall for sparing the king of the Amalekites whom Samuel had ordered killed. He predicts that David will inherit the kingdom of Israel when Saul and his sons die in the next day's battle. David learns from an Amalekite soldier of the deaths of Saul and Jonathan at the hands of the Amalekites, and David orders the Amalekite killed. After a funeral march for the Israelite dead, Merab, David, and Michal each in turn express their sorrow, particularly for the loss of Jonathan. A high priest predicts David will win future victories and the Israelites urge him to restore their kingdom.
Program and cast
Saul: Florian Boesch
David: Jake Arditti
Merab: Jasmin Delfs
Michal: Mary Bevan
Jonathan: James Ley
Abner · High Priest · Doeg: Tansel Akzeybek
Witch of Endor: Jake Ingbar
Musical Direction: Leo Hussain
Production: Claus Guth
Stage & Costumes: Christian Schmidt
Lighting: Bernd Purkrabek
Video: Arian Andiel
Choreography: Ramses Sigl
Staging: Juana Restrepo
Chorus: Jan Hoffmann
Dramaturgy: Yvonne Gebauer, Benedikt Stampfli
Saxon State Opera Chorus Dresden
Saxon State Orchestra Dresden
Semperoper Dresden
The Semperoper is the opera house of the Sächsische Staatsoper Dresden (Saxon State Opera) and the concert hall of the Sächsische Staatskapelle Dresden (Saxon State Orchestra). It is also home to the Semperoper ballet. The building is located near the Elbe River in the historic centre of Dresden, Germany.
The opera house was originally built by the architect Gottfried Semper in 1841. After a devastating fire in 1869, the opera house was rebuilt, partly again by Semper, and completed in 1878. The opera house has a long history of premieres, including major works by Richard Wagner and Richard Strauss.
The first opera house at the location of today's Semperoper was built by the architect Gottfried Semper. It opened on 13 April 1841 with an opera by Carl Maria von Weber. The building style itself is debated among many, as it has features that appear in three styles; Early Renaissance and Baroque, with Corinthian style pillars typical of Greek classical revival. Perhaps the most suitable label for this style would be eclecticism, where influences from many styles are used, a practice most common during this period. Nevertheless, the opera building, Semper's first, is regarded as one of the most beautiful European opera houses.

 EN
EN DE
DE IT
IT FR
FR ES
ES RU
RU JP
JP RO
RO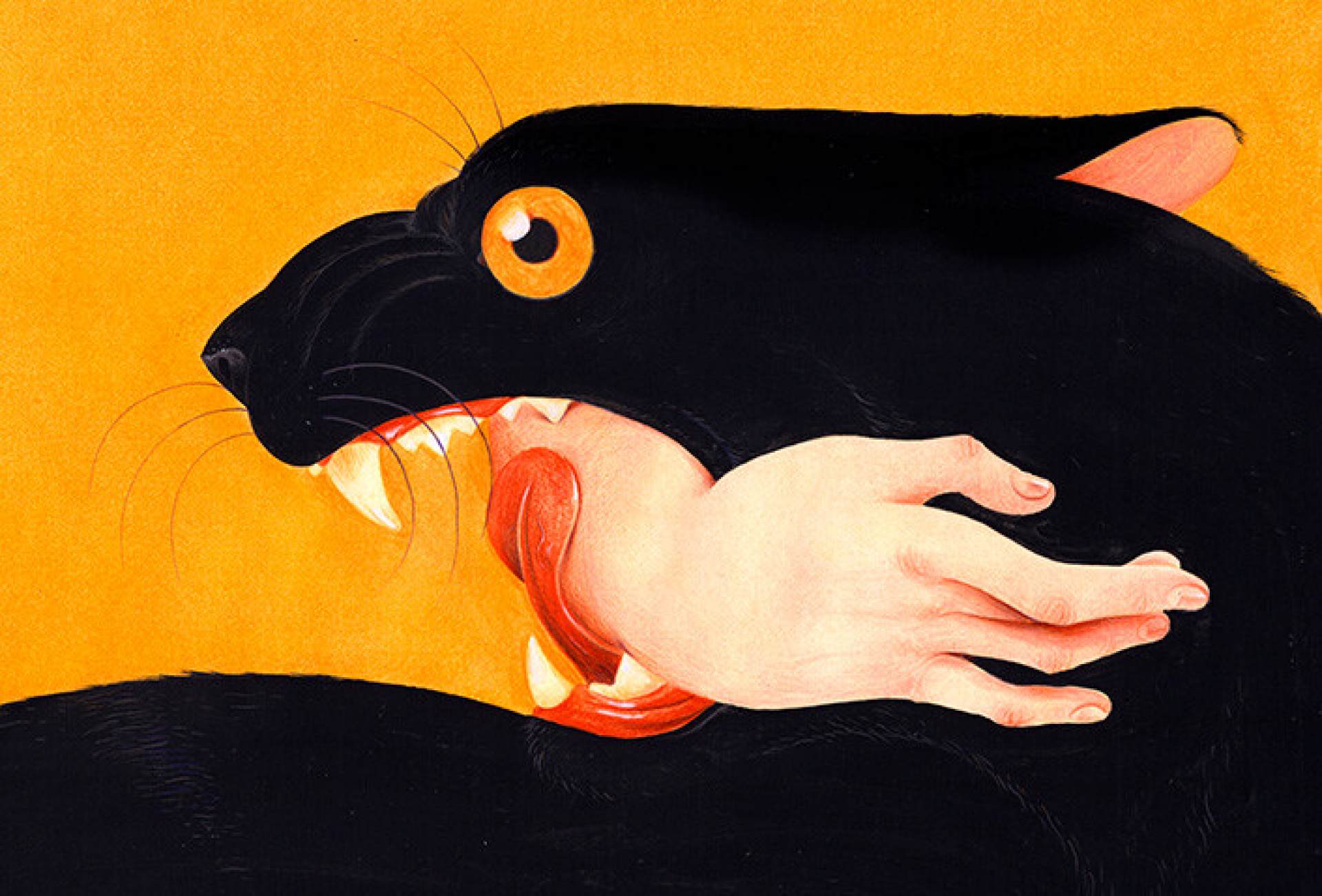
 Seating plan
Seating plan 